Eighty five samples of pleural fluid obtained from 76 patients with biopsy proven tuberculous pleurisy were examined cytologically.
Mesothelial cells in pleural fluid tb or not tb.
Pleural effusion may occur at any stage of active tuberculosis.
Mesothelial cells in pleural fluid.
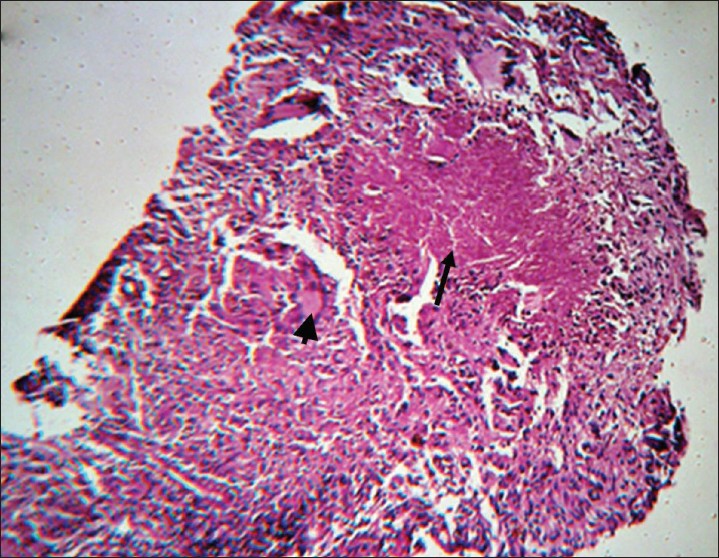
7 neutrophils 22 lymphocytes 60 macrophages and 10 mesothelial cells.
7 june 1980 sa medical journal 937 m esothelial cells in pleural fluid.
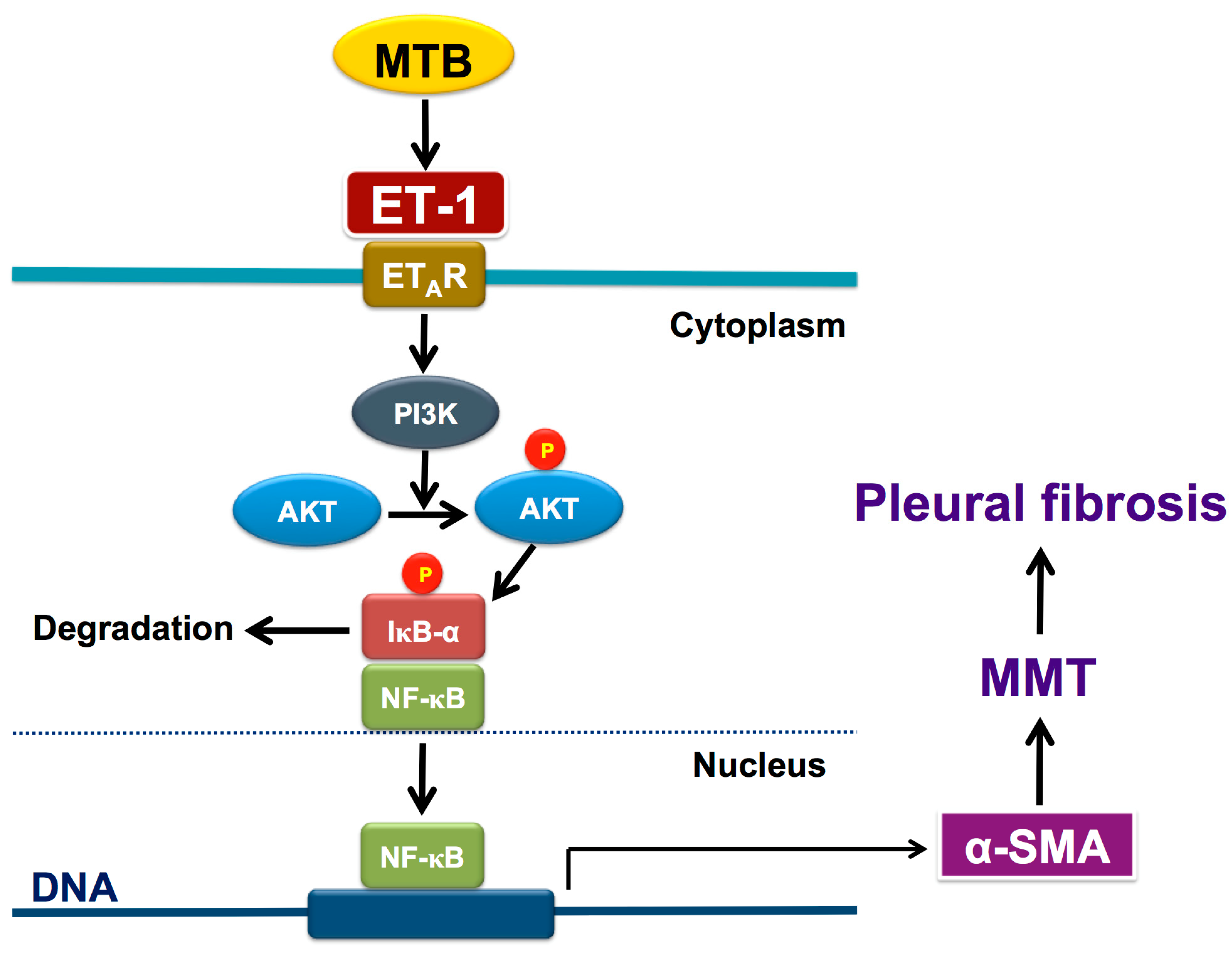
The patient was treated with a combination of six anti tb medications and was started on an antiretroviral regimen.
There are certain cells that line the pleura the thin double layered lining which covers the lungs chest wall and diaphragm which are known as mesothelial cells other than the pleura mesothelial cells also form a lining around the heart pericardium and the internal surface of the abdomen peritoneum.
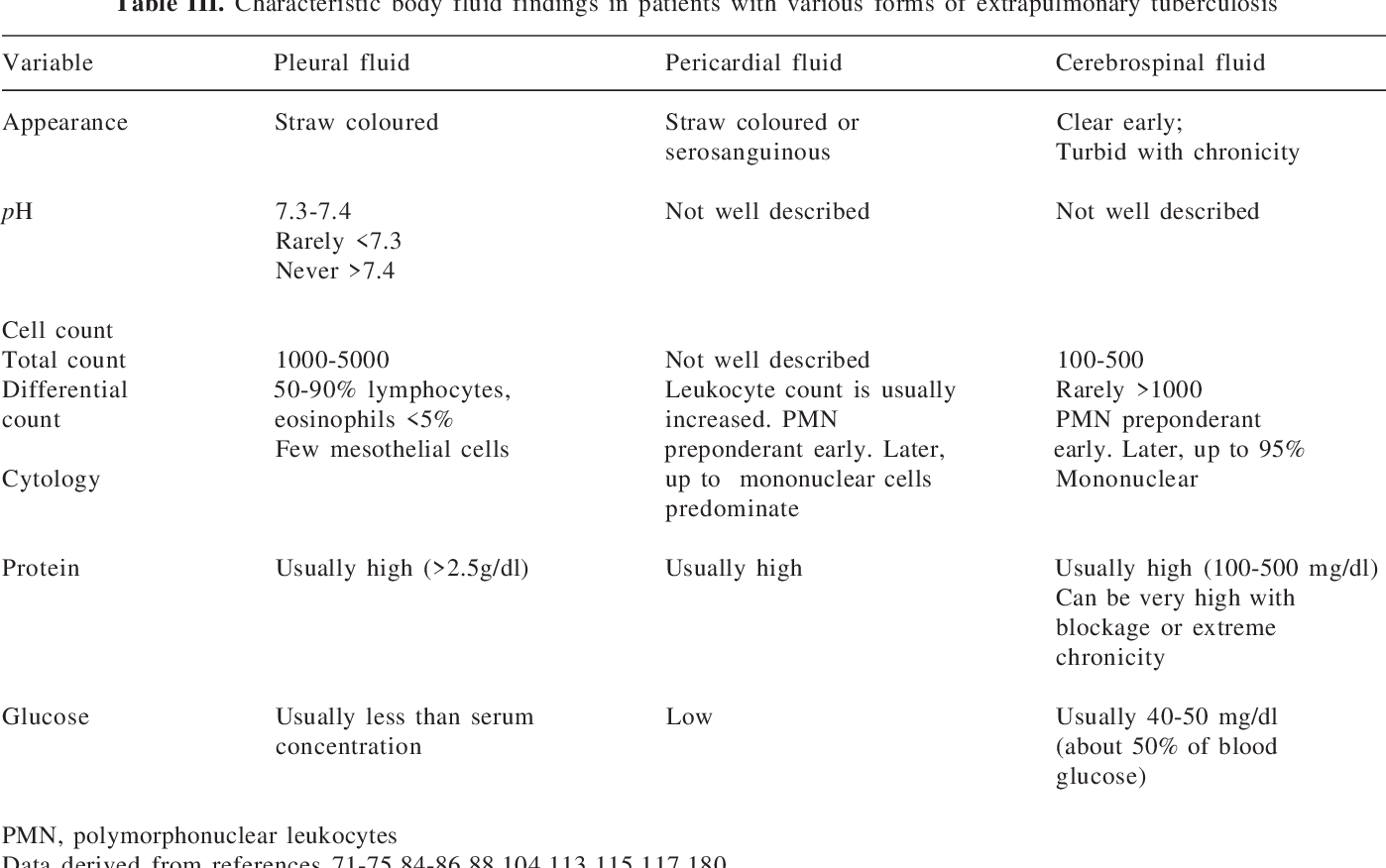
Neutrophil dominant effusions are associated with empyema or pulmonary embolism.
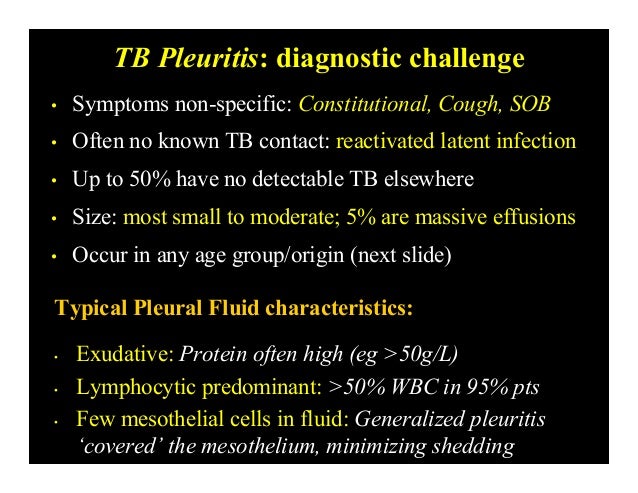
Tuberculous pleurisy is the most frequent extrapulmonary manifestation of tuberculosis.
This report concerns two cases of tuberculous pleural effusion in.
Numerous reactive mesothelial cells were present in only 1 2 of.
The suggestion that the presence of numerous often highly reactive mesothelial cells in a pleural aspirate makes the diagnosis of tuberculosis unlikely is confirmed.
Thus we were not surprised to find 16 percent of mesothelial cells in the pleural fluid.
The cytology showed reactive mesothelial cells and the differential cell count was as follows.
Eighty five samples of pleural fluid obtained from 76 patients with biopsy proven tuberculous pleurisy were examined cytologically.
Numerous reactive mesothelial cells were present in only 1 2 of specimens examined.
In contrast 65 3 of pleural fluid aspirates obtained from a control group of pati.
Hurwitz gladwyn leiman c.
Pleural fluid lymphocytosis suggests tb sarcoidosis or malignancy.
The cause of this transudative effusion is not quite clear but it would be unlikely due to tuberculosis or endoscopic esophageal sclerotherapy both of which usually give rise to exudative effusions.
Tb or not tb.
1 the pleura is a serous membrane that covers the lung parenchyma mediastinum diaphragm and rib cages and is divided into the visceral and parietal pleura.
In contrast 65 3 of pleural fluid aspirates obtained from a control group of patients in congestive cardiac failure contained marked mesothelial exfoliation.
The culture of the pleural fluid grew m tuberculosis.
White blood cells wbc results generally are not diagnostic but most transudates have wbc counts less than 1000 cells µl whereas exudates generally have wbc counts greater than 50 000 cells µl.