In this study of mfi and the related placental disorder massive perivillous fibrin deposition mfd semiquantitative histologic criteria for the.
Massive perivillous fibrin deposition maternal floor infarction.
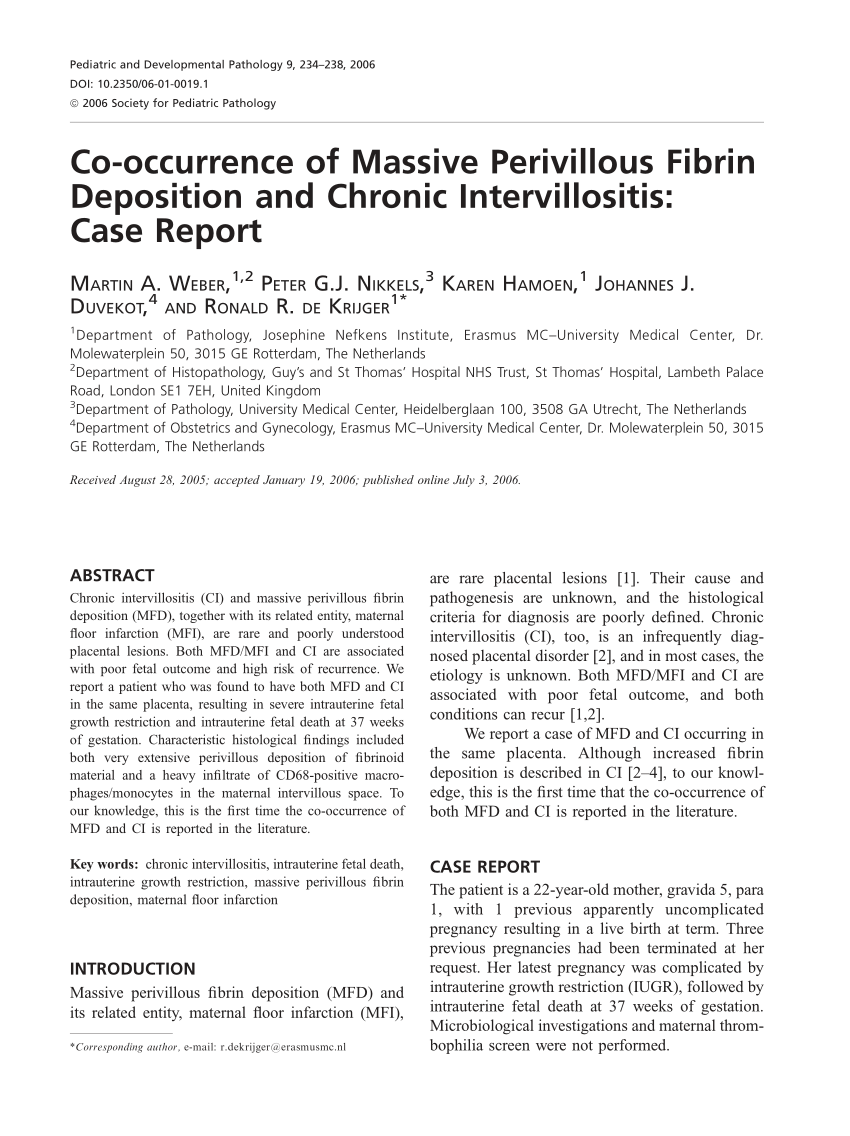
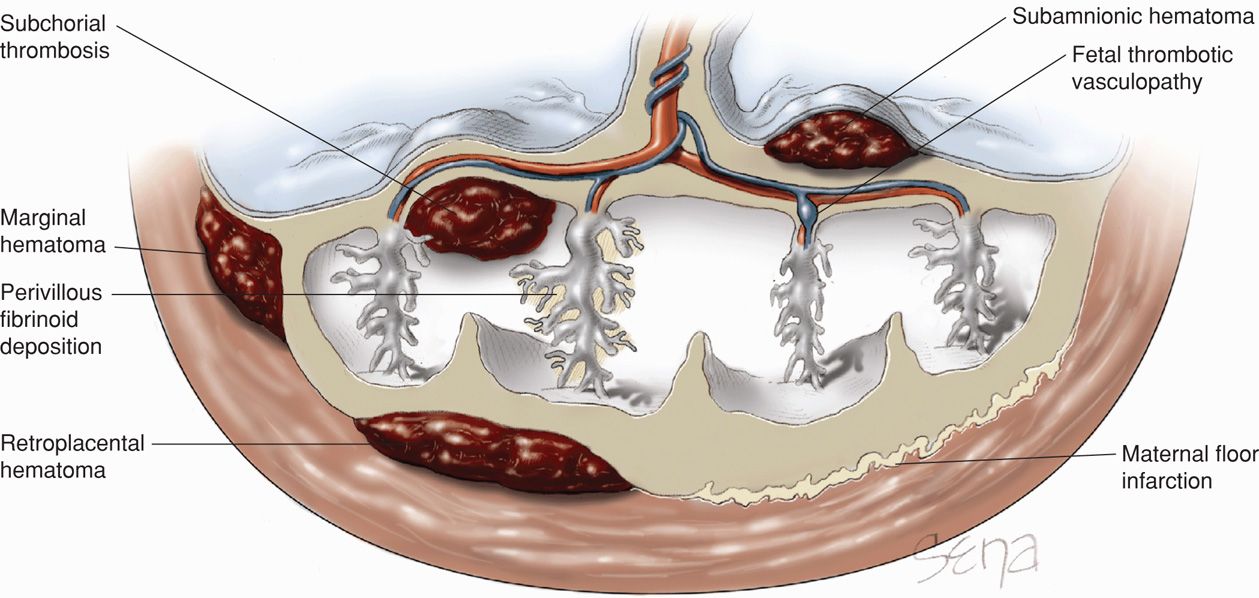
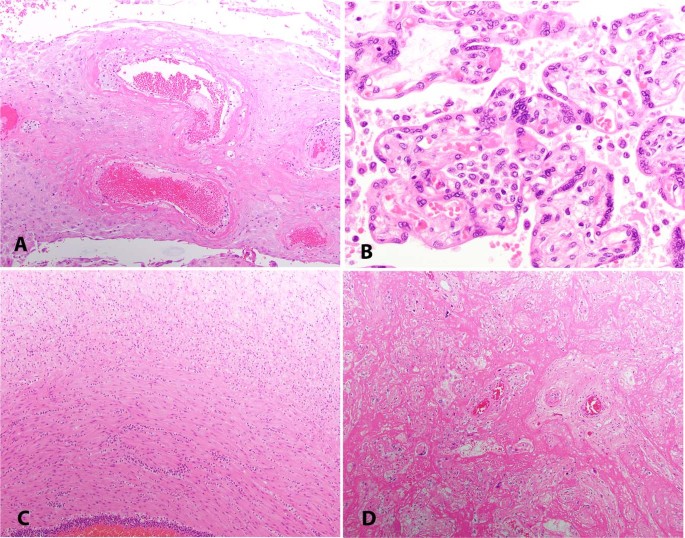
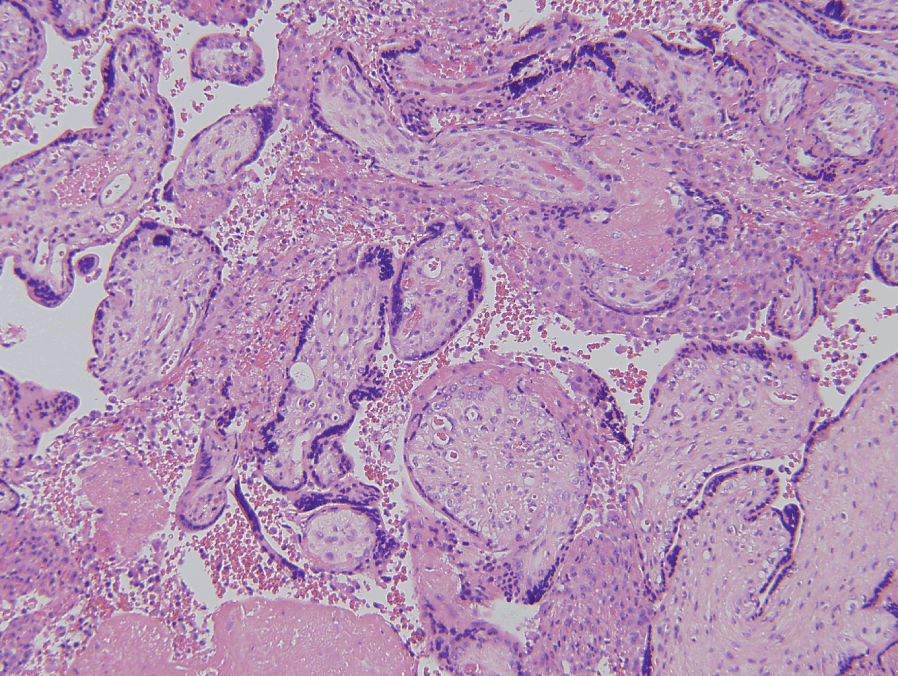
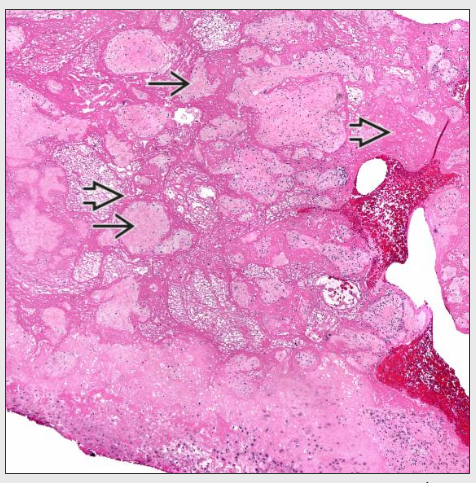
Massive deposition of intervillous fibrin that entrap the villi of the basal plate extending to a thickness of at least 3 mm may be accompanied by massive perivillous fibrin deposition associated with recurrent abortions stillbirth fetal growth restriction or neurologic impairment seen in 0 09 0 5 of placentas.
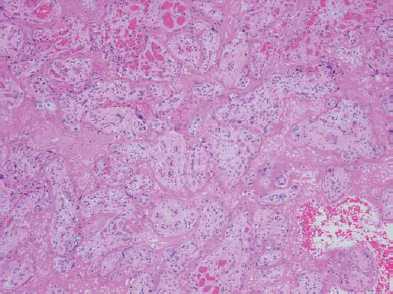
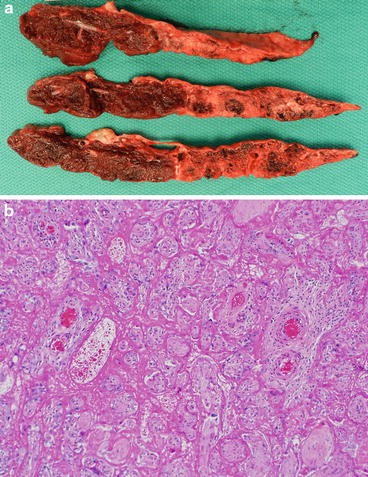
Maternal floor infarction is a similar process in which the fibrinoid material is confined to the basal villi.
Maternal floor infarction and massive perivillous fibrin deposition.
Am j obstet gynecol 1990 163 935 8.
Maternal floor infarction and massive perivillous fibrin deposition.
Katzman pj genest dr.
Massive perivillous fibrin deposition mpvfd and maternal floor infarction mfi are pregnancy complications of unknown aetiology characterised by extensive deposition of fibrin either within the intervillous space or primarily within and around the basal plate.
The association of maternal floor infarction of the placenta with adverse perinatal outcome.
The reported incidence is 0 3 0 5.
Objective massive perivillous fibrin deposition mpfd and maternal floor infarction mfi are related placental lesions often associated with fetal death and fetal growth restriction.
Maternal floor infarction mfi is a poorly understood placental lesion reportedly associated with intrauterine growth restriction iugr and recurrence.
Mpfd is a rare disorder characterized by deposition of fibrinoid material in the intervillous space leading to atrophy of the engulfed villi.
Histological definitions association with intrauterine fetal growth restriction and risk of recurrence.
Pediatr dev pathol 5 2.
Maternal floor infarction mfi is a poorly understood placental lesion reportedly associated with intrauterine growth restriction iugr and recurrence.
Maternal floor infarction mfi and massive perivillous fibrin deposition mpvfd are pathologically overlapping placental disorders with characteristic gross and shared light microscopic features of excessive perivillous deposition of fibrinoid material.
Histological definitions association with intrauterine fetal growth restriction and risk of recurrence.